
Brain Stroke : Act FAST, Save Lives
26 May 2023
Stroke
A stroke, sometimes called a brain attack, occurs when something blocks blood supply to part of the brain or when a blood vessel in the brain bursts.
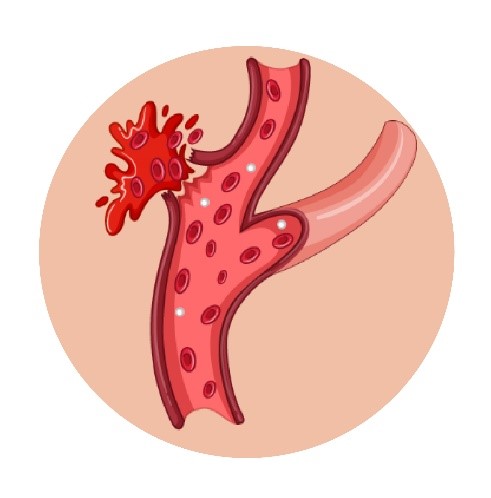
In either case, parts of the brain become damaged or die. A stroke can cause lasting brain damage, long-term disability, or even death.
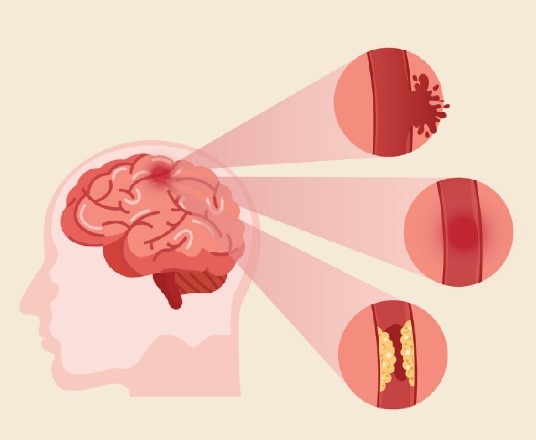
What are the types of Stroke?
There are two types of Stroke:
Ischemic Stroke
Haemorrhagic Stroke
Ischemic stroke
Most strokes are ischemic strokes.2 An ischemic stroke occurs when blood clots or other particles block the blood vessels to the brain. Fatty deposits called plaque can also cause blockages by building up in the blood vessels.
Haemorrhagic Stroke
A haemorrhagic stroke happens when an artery in the brain leaks blood or ruptures (breaks open). The leaked blood puts too much pressure on brain cells, which damages them.
High blood pressure and aneurysms balloon-like bulges in an artery that can stretch and burst are examples of conditions that can cause a haemorrhagic stroke.
What are the symptoms of a brain stroke?
What are the symptoms of a brain stroke?
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Sudden confusion
- Trouble speaking
- Difficulty understanding speech
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness
- Loss of balance or lack of coordination
- Sudden severe headache with vomiting or unconsciousness
Sudden severe headache with vomiting or unconsciousness
Time is brain. With a stroke time lost is brain lost
The estimated pace of neurons lost in acute ischemic stroke per minute is 1.9 million neurons, per hour is 120 million and per stroke around 1.2 billion cells are lost. This is the reason for early identification of stroke symptoms and early intervention to prevent long-term disability.
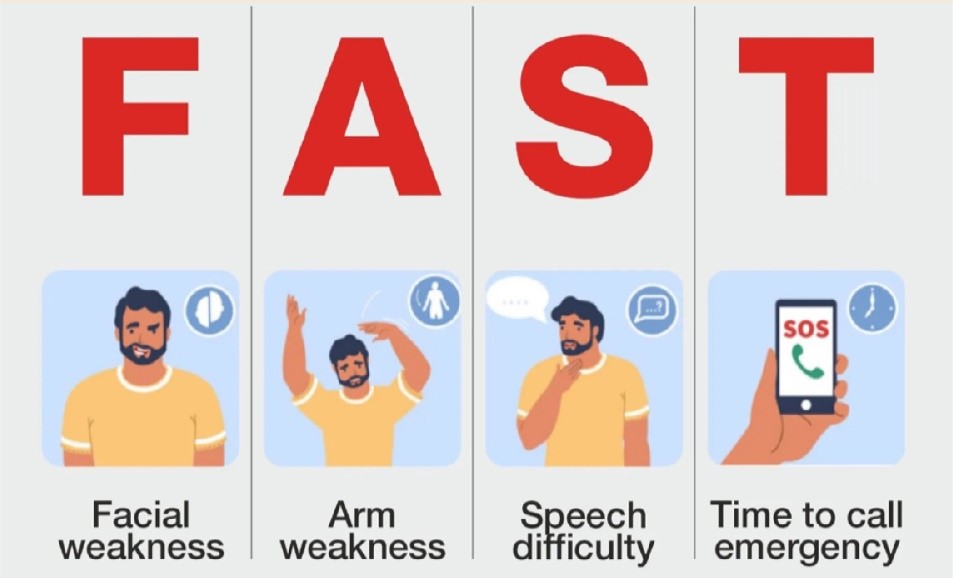
Act FAST at the first sign of stroke. We can use these letters F.A.S.T. to spot the signs of stroke and know when to call emergency.
Act FAST at the first sign of stroke. We can use these letters F.A.S.T. to spot the signs of stroke and know when to call emergency.
You should visit a Neurologist (or Hospital having Neurologist) and go to the nearest Emergency Room if you experience any symptoms of another stroke (see the FAST criteria at this article to know the symptoms for which you should watch).